

Green AI is a practical idea: build and run AI with less energy and less waste, without wrecking quality. It covers how you train models, how you deploy them, and how you measure impact in day-to-day operations.
At first, it can sound like a branding term. Then you look at how many models get trained, retrained, and served at scale, and it starts to feel like an engineering budget problem too.
DOE estimates data centers used 4.4% of total U.S. electricity in 2023. Power bills, GPU time, cooling, and capacity planning are real constraints. Green AI is simply the set of habits that stop those constraints becoming your bottleneck.
The best part is that most Green AI wins are not “big research breakthroughs.” They are small design choices that add up: smaller models, smarter data, better scheduling, and tight evaluation so you do not train five times just to feel confident.
This guide breaks down what Green AI means, how it improves energy efficiency in real systems, and how teams use AI for carbon emission tracking without turning it into spreadsheet theatre.
Green AI means building AI systems that use fewer resources per useful outcome. The outcome can be accuracy, latency, business value, or safety. The “green” part is the resource discipline around that outcome.
It is close to Sustainable AI, but Sustainable AI often includes the full lifecycle view. That includes hardware sourcing, data centre choices, and operational policies. Green AI stays closer to the technical choices teams make every week: training strategy, model selection, and inference optimisation.
A simple mental model helps. Ask this question: “How much energy do we spend to get this feature working and keep it working?” Green AI is the work that brings that number down, while keeping the feature reliable.
Most AI costs do not sit in a single training run. It sits in repetition. EIA projects commercial computing electricity use growth.
A model gets trained, then tuned, then retrained because data drift shows up, then served 24/7. Even a modest model can end up expensive if it runs at high traffic. This is where green computing benefits for businesses become real, because waste shows up as bills and capacity limits.
Green AI reduces waste in three places:
You might think the only reason to care is climate impact. That is part of it, but it is also uptime and margin. If your AI feature needs double the hardware you expected, finance will notice before your users do.
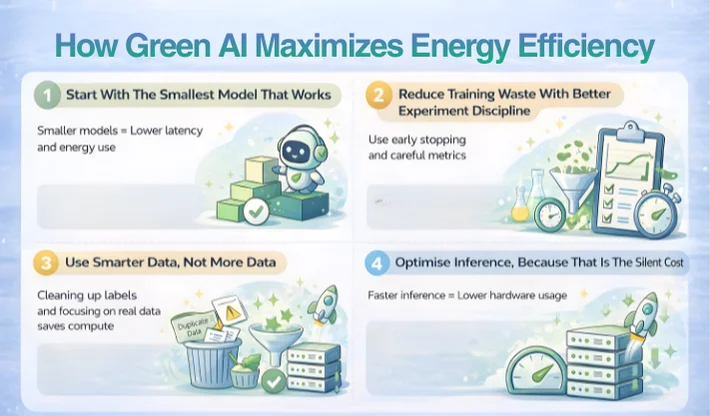
Energy efficiency in AI is not one trick. It is a set of choices that reduce compute per result.
A bigger model can feel safer, but it can also be lazy engineering. Many product tasks do not need a giant model. Classification, extraction, routing, and short summarisation often work well with smaller models or task-specific models. The practical mindset behind Eco-friendly AI sustainability is picking the smallest model that clears your quality bar.
This is also where Eco-friendly artificial intelligence becomes practical, not philosophical. If a small model hits your quality bar, you get lower latency and lower energy use in one shot.
A lot of energy gets burned in experiments that never ship.
The fix is boring but powerful:
Even a simple early-stopping rule can save a lot of compute across many runs. For a simple playbook, these 10 ways to apply green computing fit well with how teams run experiments.
More data is not always better. Better data is.
Cleaning labels, removing duplicates, and focusing on data that matches real usage often reduces training time because the model learns faster. You also avoid bloated pipelines that keep chewing power during every retrain.
Training gets the attention, but inference is often the long-term bill.
If your model serves thousands of requests per minute, shaving a few milliseconds and a bit of memory per request can cut hardware needs significantly. To keep this measurable and auditable, pair optimisation work with basic AI data governance on logs, access, and evaluation sets.
This is where Energy-efficient machine learning becomes a product advantage. You can offer faster experiences on the same budget.
Part of you might think Green AI equals “just use smaller models.” That helps, but it is not the full picture.
If you use a small model and retrain it every day without reason, you still waste compute. If you deploy a small model with messy prompts that cause retries, you still waste compute. If your pipeline logs too much data, you still pay for storage and processing.
Green AI is really about system behaviour. You want fewer wasted cycles, fewer repeated runs, and fewer surprises.

Green AI clicks once you tie it to real team moments. Pick one feature and measure cost per useful outcome, not vague effort. Track energy or spend per 1,000 inferences, or per training run that clears the quality bar. This keeps debates grounded and makes trade-offs easier.
Most waste is not one huge training run. It hides in constant iteration and overprovisioned serving. If your app has heavy traffic, start with inference. Quantisation, caching, and routing often cut compute quickly while keeping quality steady for real users.
Build habits that prevent waste, not just one-off fixes. Set limits on experiments, retries, and run frequency. Review outliers weekly and stop runs when gains are tiny. This keeps costs predictable so finance and ops can plan with confidence.
Most teams do not need a lecture on sustainability. They need a plan that keeps AI features fast and affordable.
WebOsmotic helps teams design Energy-efficient Machine Learning pipelines, choose the right model sizes, and set up routing so small models handle the common path. We also help teams implement AI for carbon emission tracking in a way that supports real decisions, not just dashboards. If logistics is your biggest lever, AI logistics automation can reduce fuel waste with better routing and smarter planning.
If your AI costs are rising and you are not sure why, the usual answer is hidden waste in serving, retraining, and retries. Fixing those often gives the fastest win.
Green AI is the practice of building and running AI with lower energy use per useful result.
They overlap. Sustainable AI often includes the full lifecycle view, while Green AI focuses more on training and deployment efficiency.
In many products, inference optimisations give the fastest win because serving runs all day. Quantisation, caching, and routing help a lot.
It can if you shrink models blindly. The safer approach is to measure end-to-end outcomes and use techniques like distillation and routing.
It helps estimate emissions, spot anomalies, and point teams to operational fixes that reduce energy waste and cost.